Nowadays, analytical solutions are becoming mission critical for many organizations. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services (SSAS) is designed to provide exceptional performance and scalable support with millions of records and thousands of users from different locations.
Why to Build a Cube?
There are many advantages of cube over relational data mart.
- While querying a data mart, you can get most of the results but not everything you need for business analysis and decsion making. Cube can help you to get answers of all "What-If" scenarios.
- Building a cube helps to house your data to centralize the business rules for calculations that you can't easily store in a relational data mart.
- The structure of the cube makes it much easier to write queries to compare data year over year (YOY), or to create cumulative values such as year-to-date (YTD) sales.
- Scalable Infrastructure - Analysis Services can scale to support databases of many terabytes in size with many thousands of users.
- Superior Performance - Analysis Services cubes are multidimensional structures that enable fast access to high volumes of pre-aggregated data, empowering end users to gain insight into relevant business data at the speed of thought.
- You gain the ability to manage aggregated data in the cube. To improve query performance in a relational data mart, we often create summary tables to prepare data for queries that don't require transaction-level detail. SSAS creates the logical equivalent of summary tables (called aggregations) and keeps them up-to-date.
I would like to introduce beginners to Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) by creating a simple cube from AdventureWorksDW2008R2. You can install this database from codeplex. I'll cover following things in this article:
- Creating Analysis Services Project
- Creating Data Source
- Creating Data Source View
- Creating Cube and Dimensions
- Creating Dimension Hierarchies
- Deploying Cube Database from BIDS
Creating Analysis Services Project.
First step is to create a project in Business Intelligence Development Studio (BIDS). Launch BIDS from Start --> All Programs --> Microsoft SQL Server 2008 --> SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio and then click File --> New --> Project. In the New Project dialog box, select Analysis Services Project. In the Name text box, type LearnSSAS and, if you like, change the location for your project. I'll store this project at location D:\Hari. Click OK to create the project.
Creating Data Source
Now add a data source to define the connection string for data mart AdventureWorksDW2008R2. In Solution Explorer, right-click the Data Sources folder and click New Data Source.
In the Data Source Wizard, click Next on the Welcome to the Data Source Wizard page if it hasn't been disabled. On the Select how to define the connection page, click New to set up a new connection. In the Connection Manager, the default provider is the Native OLE DB\SQL Server Native Client 10.0, which is correct for our project.
To define the connection, type the name of your server in the Server Name text box. Alternatively you can select it from the drop-down list, then select AdventureWorksDW2008R2 in the database drop-down list and click Test Connection button to check the connection. Finally click on OK as shown below:
When you're back in the Data Source Wizard, click Next. On the Impersonation Information page, select Use the service account option so that service account will be used to read data from the source when loading data into your SSAS database and service account must have read permissions to do so. Click Next and then Finish to complete the wizard.
Creating Data Source View
Now next step is to create a
data source view (DSV) from the data source to define dimensions and cubes. You can make changes to the DSV without modifying the actual data source, which is very useful if you have only read permissions to the data mart. In
Solution Explorer, right-click on the
Data Source Views folder and then click
New Data Source Views...You can see
Data Source View Wizard. Click Next on the Welcome page. On the
Select a Data Source page, select the data source just added to the project (Adventure Works DW2008R2.ds) and click
Next. Now add required objects to the DSV by double-clicking each table or view on
Select Tables and Views page. I want to add the following tables to the DSV to make it easy to understand for beginners:
DimDate, DimProduct, DimProductCategory, DimProductSubcategory, and FactInternetSales. You can always add more tables later if you want to explore advance BI questions. Now click Next in the Data Source View Wizard once you are finished adding required tables followed by click on Finish. You can give a name to your DSV before clicking Finish button.
I would recommend you to change the name of objects by selecting each one in the DSV designer and remove the Dim and Fact prefixes from the FriendlyName property because when you create dimensions and cubes, only FriendlyName property will be assigned to the objects.
The DSV is shown below:
Creating Cube and Dimensions
Next step is to create a Cube and Dimensions from the data source view. In Solution Explorer, right-click on the Cubes folder and then click New Cube...You can see Cube Wizard. Click on Next in Welcome to the Cube Wizard page.On the Select Creation Method page, keep the default option Use existing tables and click Next button. On the Select Measure Group Tables page, choose InternetSales table and click Next.
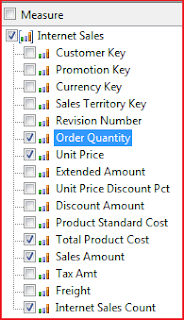
Now the wizard displays all the measures available in the selected measure group tables. Measures are basically numeric values e.g. OrderQuantity, Unit Price, Sales Amount, Tax Amount etc. Select only the following measures from Internet Sales Group: Order Quantity, Unit Price, Total Product Cost, Sales Amount, and Internet Sales Count
Now click on Next button to open Select New Dimensions page and select Date and Product dimensions. Click Next to proceed.
In the Completing the Wizard page, enter the cube name as AdventureWorksCube and click Finish button to complete the wizard. Cube layout is shown below:
Now click on each dimensions and add required attributes from the Data Source View.
Date Dimension:
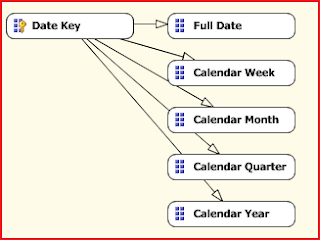
Drag and drop FullDateAlternateKey, CalendarYear, CalendarQuarter, EnglishMonthName, and EnglishDayNameOfWeek. Rename FullDateAlternateKey with Full Date, EnglishMonthName with Calendar Month, and EnglishDayNameOfWeek with Calendar Week as shown below:
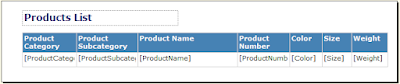
Product Dimension:
Drag and drop EnglishProductCategoryName from ProductCategory table, EnglishProductSubcategoryName from ProductSubcategory table and Color, ModelName, Size and Weight from Product table.
Creating Dimension Hierarchies
Navigate to Date Dimension Structure. Drag and drop
Calendar Year attribute into
Hierarchies surface area following by
Calendar Quarter, Calendar Month, Calendar Week , and Full Date attributes.
Rename hierarchy with Calendar. You'll see a warning mark in the hierarchy because attribute relationship is not set properly.
Set Attribute Relationships
Click on the Attribute Relationships tab in the dimension designer. This tab is available only in Analysis Services 2008. By default, all attributes relate directly to the key attribute, Date Key as shown below:
To optimize the design by reassigning relationships, Right Click on Full Date and select New Attribute Relationship. Select Related Attribute as Calendar Week and Relationship type as Rigid (will not change over time). Repeat same thing for remaining attributes. Finally Attribute Relation will look like below image:
Deploying Cube Database from BIDS
Now its time to deploy the cube at required server. Right click on the project (LearnSSAS in this example) and click properties to open project properties page. Enter Server Name name Server property and Database name in Database property as shown below:
Click OK to save changes. Now right click on the project and click on Process to Build and Deploy the project. You will a message while deploying the database first time.
Click on Yes to proceed. Now you can see Process Database - PreojectName window. Click on Run to continue.
Once the database is deployed and processed successfully, you can see the data through Browser tab or directly through SQL Server Analysis Services. You can also pull cube data in Excel using Excel OLAP Pivot Tables, which is the prefered option used by business managers.